What are the features of each deployment option?
In today's fast-paced business environment, efficient management of resources is crucial for success. Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems have emerged as a powerful solution for small and medium-sized businesses (SMBs) to streamline operations and improve decision-making.
ERP systems enhance productivity and enable better control over processes by integrating various business functions into a centralized platform. With a range of options available, including on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid ERP solutions, SMB owners need to understand their differences to make an informed decision.
In this blog post, we will explore each solution's features, advantages, and disadvantages, providing valuable insights to help you choose the right ERP system for your business.
ON-PREMISE ERP SYSTEMS
The On-premise addition of ERP systems are installed locally on a company's own servers and managed by the internal IT department. This traditional approach to ERP allows businesses to have full control over their data and infrastructure.
DEFINITION AND EXPLANATION
On-premise ERP systems are software solutions that are installed and run on a company's in-house hardware, such as servers and workstations. 3rd party companies are responsible for maintaining and managing the infrastructure and software, which includes handling updates, patches, and security measures.
ADVANTAGES
- Greater Control Over Data and Security: With an on-premise ERP system, businesses have complete control over their data, allowing for increased security measures tailored to the company's requirements. This level of control is particularly advantageous for organizations that deal with sensitive data or operate in highly regulated industries.
- High Level of Customization and Flexibility: On-premise ERP solutions allow businesses to fine-tune the system according to their particular processes and requirements. This flexibility enables organizations to develop a bespoke solution that addresses their unique needs and promotes increased efficiency and seamless operation.
- One-time Investment: Although initial costs can be high, on-premise ERP systems typically require a one-time investment, which may result in long-term cost savings. Over time, the total cost of ownership may be lower compared to cloud-based solutions, which require ongoing subscription fees.
- Independence from Internet Connectivity: On-premise edition operate independently of internet connections, ensuring that businesses can continue functioning even during internet downtime. This can be particularly beneficial for organizations that operate in areas with unreliable internet service.
DISADVANTAGES
- Significant Upfront Costs: On-premise deployments come with high initial costs for hardware, software, and implementation services. These costs can be prohibitive for smaller businesses or those with limited budgets.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Updates: Companies are responsible for managing and maintaining the system, which can be resource-intensive and time-consuming. This may require dedicated IT personnel and additional investment in hardware and software maintenance.
- Limited Scalability: Scaling on-premise ERP systems may require additional hardware investments and complex infrastructure upgrades. This can make it difficult for businesses to quickly adapt to changing needs and market conditions.
- Lack of Mobility: On-premise ERP systems typically require users to be physically present in the office to access the system. This can limit the flexibility and mobility of employees, particularly in today's increasingly remote work environment.
CLOUD-BASED ERP SYSTEMS
Cloud-based ERP systems are hosted by a third-party provider and accessed via the internet, and come with great benefits. This means the provider is responsible for maintaining the software and infrastructure, allowing businesses to focus on their core operations.
DEFINITION AND EXPLANATION
Cloud-based ERP systems are software solutions that are hosted on a third-party provider's servers and accessed through the internet. The provider handles infrastructure maintenance, software updates, and security measures, freeing up businesses to focus on their core functions.
ADVANTAGES
- Lower Initial Costs: Cloud deployment generally have lower upfront costs compared to on-premise solutions, as they do not require investments in hardware and software. This makes it a more affordable option for small businesses and startups with limited budgets.
- Easy Scalability: The cloud version offers seamless scalability, making it simple for businesses to expand or contract their operations as needed. This allows organizations to quickly adapt to market changes and growth opportunities without significant investments in infrastructure.
- Automatic Updates: The provider is responsible for maintaining the software, which includes regular updates and patches, ensuring that businesses always have access to the latest features and improvements. This can save time and resources that would otherwise be spent on manual updates and maintenance.
- Mobility and Accessibility: Cloud deployments can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, providing greater flexibility and mobility for employees. This enables remote work and supports collaboration between team members, regardless of their physical location.
DISADVANTAGES
- Dependency on Provider's Security Measures: Businesses must rely on the third-party provider's security measures and protocols, which may not always align with the company's specific needs. This can be a concern for organizations that handle sensitive data or require high levels of security.
- Limited Customization: The cloud version typically offer less customization than on-premise solutions, which may be a disadvantage for businesses with unique processes and requirements. While many providers offer a range of features and modules, it may not be possible to tailor the system as extensively as with an on-premise solution.
- Potential Connectivity Issues: As cloud-based ERP systems are accessed via the internet, businesses may experience connectivity issues or downtime due to internet-related problems. This can disrupt operations and may impact the system's overall efficiency.
HYBRID ERP SYSTEMS
Hybrid ERP systems combine the best of both worlds, offering a mix of on-premise and cloud-based components. This approach enables businesses to maintain control over critical data while benefiting from the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud solutions.
DEFINITION AND EXPLANATION
Hybrid ERP systems are software solutions that incorporate both on-premise and cloud-based components, providing businesses with a flexible approach to managing their operations. Companies can choose which functions and data are managed on-site and which are hosted in the cloud, offering a balance between control and scalability.
ADVANTAGES
- Balance of Control and Scalability: Hybrid ERP systems provide businesses with the control and security of on-premise solutions while offering the scalability and cost-effectiveness of cloud-based systems. This enables organizations to create a tailored ERP solution that meets their specific needs and requirements.
- Customization Options with Cloud Benefits: Hybrid ERP solutions enable businesses to enjoy the benefits of customization available in on-premise solutions, combined with the convenience of cloud-based features, such as automatic updates and accessibility. This can result in a more efficient and cost-effective ERP system that caters to the organization's unique needs.
- Adaptability: Hybrid ERP systems offer businesses the ability to adapt to changing circumstances and requirements, making it easier to transition from on-premise to cloud-based solutions or vice versa as needed. This flexibility can be particularly beneficial in industries that experience rapid change or growth.
DISADVANTAGES
- More Complex Implementation Process: Implementing a hybrid ERP system can be more complex than adopting a purely on-premise or cloud-based solution, as it requires integration and management of both types of components. This may result in a longer implementation timeline and increased costs.
- May Require Additional Resources: Managing a hybrid ERP system effectively may necessitate additional resources, such as specialized IT personnel or expertise in both on-premise and cloud-based systems. This can increase the overall cost and complexity of the system.
COMPARING ON-PREMISE, CLOUD-BASED, AND HYBRID ERP SYSTEMS
To help you better understand the key differences between on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid ERP systems, we have created a comparison table highlighting their main features, advantages, and disadvantages.
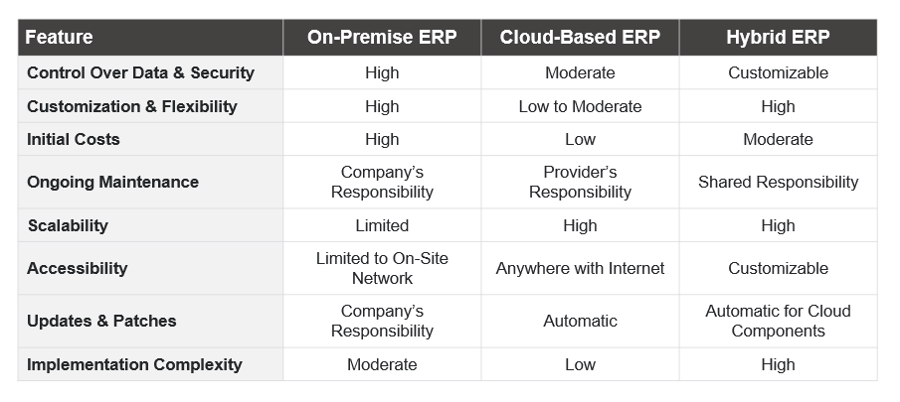
Factors to consider when choosing an ERP system for your business include cost, customization, security, scalability, accessibility, and the level of control you require over your data and infrastructure.
CONCLUSION
Selecting the right ERP system for your SMB is a critical decision that can significantly impact your company's efficiency, growth, and long-term success. By understanding the nuances of on-premise, cloud-based, and hybrid ERP solutions, you can choose the best option for your business requirements.
Whether you opt for the control and customization of an on-premise ERP system, the scalability and cost-effectiveness of a cloud-based solution, or the adaptability of a hybrid approach, the key is finding a system that meets your unique needs and helps you streamline your operations.
Investing in the right ERP system is an investment in your business's future. Take the time to evaluate your options carefully, considering both your choice's short-term and long-term implications. Ultimately, the best ERP solution will improve efficiency and productivity and position your business for sustained growth and success.
